The country of Greece was recently in the news for all the right reasons of introducing pocket parks in its capital city, Athens. These ecological parks are created in the densely populated localities of Kypseli, Kolonos and Pagrati to subsequently address environmental issues such as urban heat island effect and pollution, while also attempting to bring uniformity in the distribution of green spaces across the city.
Pocket parks, initially known as vest-pocket parks are mini regular parks. Usually set up in urban sprawls, they cater to the immediate local population. The predominant feature of a pocket park design is, not much space is required to build them like in the case of Athens, where existing garbage dumps and weed-filled spots were utilized to create these mini parks.
While the idea of pocket parks has been floating around for some years now, it’s only until recently that countries have actually begun adopting this concept. Greece is one such country to implement the idea. Some famous pocket parks of the world are Greenacre Park (New York City, US), Place Dauphine (Paris, France), Franklin Street Park (Massachusetts, US) and now, the pocket parks in Athens.
With rapid trend in urbanization and threat of climate change, the concept of vest-pocket parks is steadily gaining popularity. Not only do pocket parks provide the desired sustainability outcomes, but also, their construction can be carried out in an environment-friendly manner that can further complement the design and intent of these parks. The building materials used can be sourced locally to reduce the financial cost as well as the carbon footprint. Porous concrete can be used for walkways to enable the absorption of adequate water and air by the trees from the soil. Sustainably sourced woods, strawbales, recycled steel, bamboo, rammed earth, etc. are also ideal raw materials for the construction of pocket parks.
Furthermore, the ground beneath pocket parks can be a great place to install geothermal heat pumps. The energy sourced from these parks can then be supplied to the neighboring buildings for heating and cooling purposes. This, in turn, can reduce the grid energy consumption and therefore bring down the carbon emissions of that area.
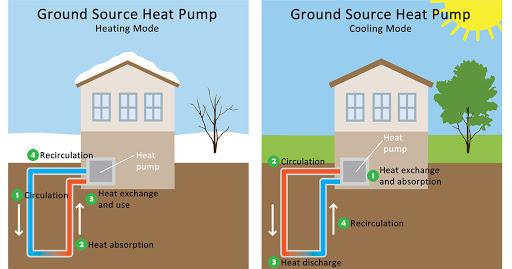
Image: A guide to how a geothermal pump works for heating and cooling purposes
The parks in the city of Athens have adopted the use of green materials. The concrete used to build the ground surface and sidewalks are eco friendly while, recycled wood has been utilized to construct the seating areas. An underground irrigation system is used to water the entire vegetation in a single park. Photovoltaic panels have been installed to illuminate the parks at night as well as run the digital panels to display temperature, humidity and other environmental parameters of the surrounding area. As of March 2021, three pocket parks are functioning in the country by way of public access while ten such parks are in the pipeline to be developed by the end of this year.

Image: Pocket Park in Athens
Athens, also known as the summer capital of Europe earlier used to witness a mild mediterranean climate with maximum summer temperatures reaching 35/36 °C (95/97 °F). With the increase in population and number of vehicles, urban heat island effect has now become a noticeable phenomenon. During a heatwave, temperatures in summer now go up to 40°C (104 °F) in Athens.
The introduction of pocket parks is therefore considered to be a significant step towards combating the effects of climate change and global warming. In addition to this, the city administration has also been praised for undertaking initiatives like allocation of 50,000 square metres of public space for cyclists and pedestrians, widening of pavements, pedestrianization of boulevards (tree lawns) and enlargement of squares.
Abandoned water fountains are being repaired and restored to lower the local temperatures and improve air quality. So far, the residents of Athens have expressed great content with these developments. I believe that these nature-based design solutions are meaningful and strategic to improve the natural environment and ecology of the city of Athens.
Pocket parks are not a ‘location-specific’ limited concept but can also be adopted by malls, hospitals, offices, schools, restaurants, hotels, private residences, etc. With numerous pocket park design guidelines available on the internet, construction of more parks can be undertaken which is guaranteed to return a good quality of life from a comparatively low investment.
Additionally, new and existing techniques such as GrowMore (a clever planter that expands as a garden grows), small-scale biogas digesters (helps produce energy and fertilizer by the process of anaerobic digestion of garden wastes) and rain barrels (to store rainwater in drought-prone regions) can be adopted in the pocket parks. The integration of such new and existing technologies can add significant value to the already existing pocket park benefits.
Green urban spaces as a natural solution has been observed to encourage sustainable living, improve quality of life and improve the overall resilience of cities and their inhabitants. In my opinion, pocket parks are an excellent example of optimization of green spaces, especially in densely populated cities. Equal distribution of green spaces is known to combat mental health issues like depression and anxiety, thereby playing a significant role in the well-being of urban residents.

Image: Impacts of urban green spaces on health and well-being
Several research also show that the physical and mental health, especially of those people living fast-paced city lives is directly influenced by their surrounding natural ambiance. The incorporation of mini parks can make communities safer and sociable, while also providing the local people a sense of ownership by turning them into community decision-makers.
To conclude, it is high time that cities need to break the stereotype of concrete jungles as urbanization and reconsider incorporating urban green spaces as an integral part of the overall urban planning process.


Very good article. I certainly appreciate this website. Keep writing!
We have been visiting variousblogs for my dissertation study. Ive discovered your blog being quite beneficial.
Keep up the good work but I was just wondering where ideally we should or need to install such pocket parks or which is most suitable place to install these in India.Futhermore can we also install these in hilly terrain,I am just curious.
Hey! Thanks for the comment 🙂 we can definitely install these on hilly terrains! Either for hilly or plain terrains, we can build these parks in any used space. Since they need little space, they can be constructed in abandoned public spaces, rooftops, small alleys and so on.